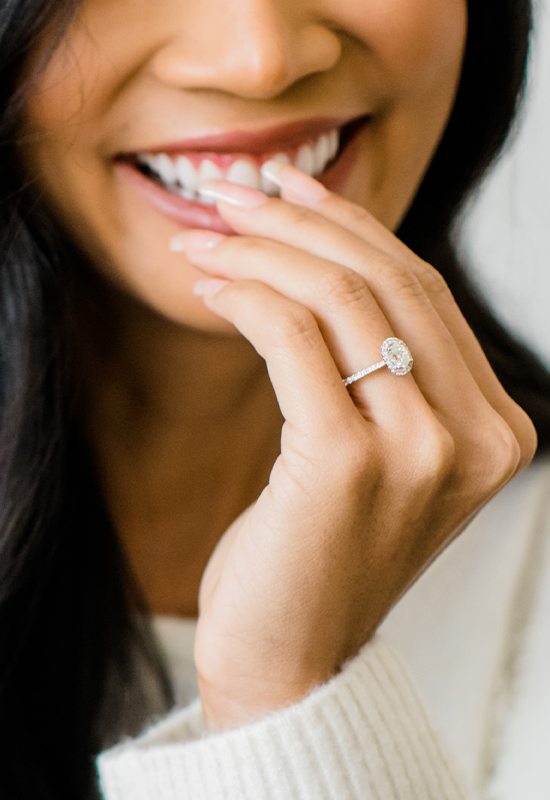
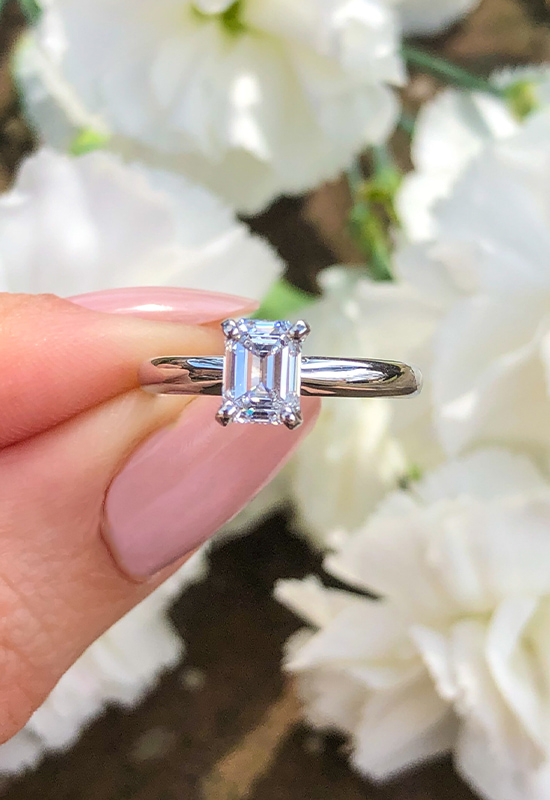
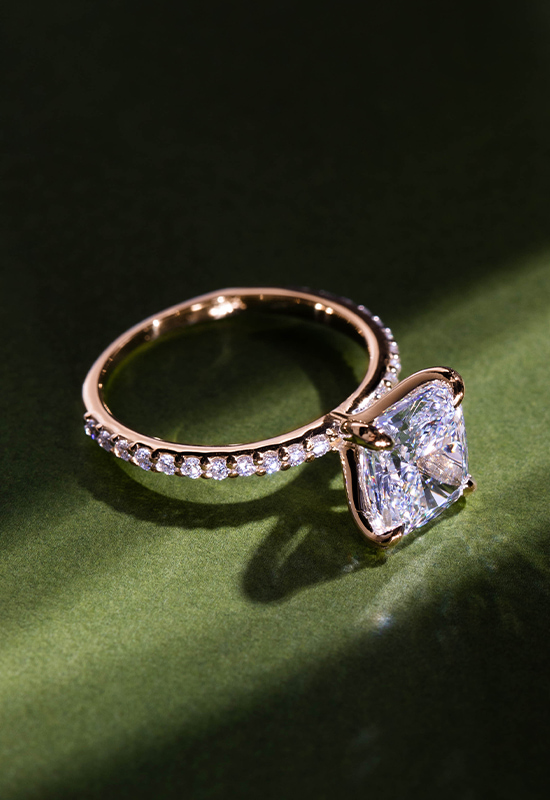
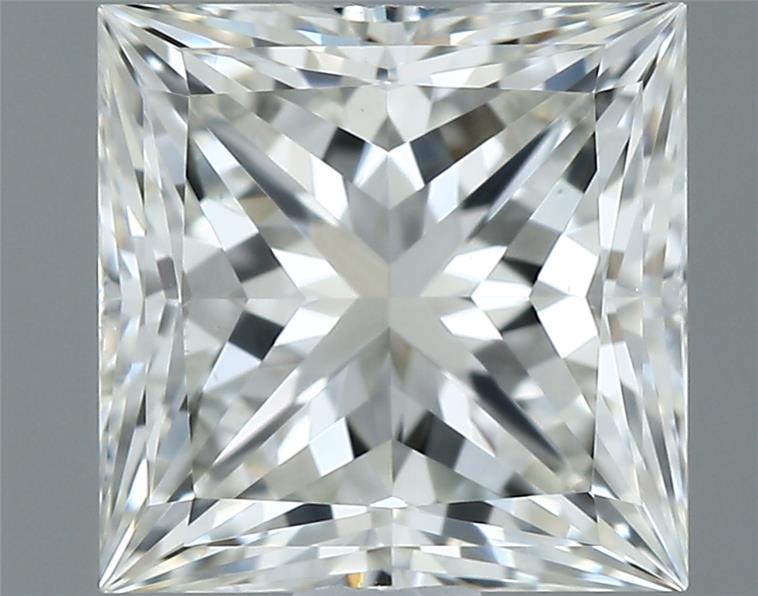
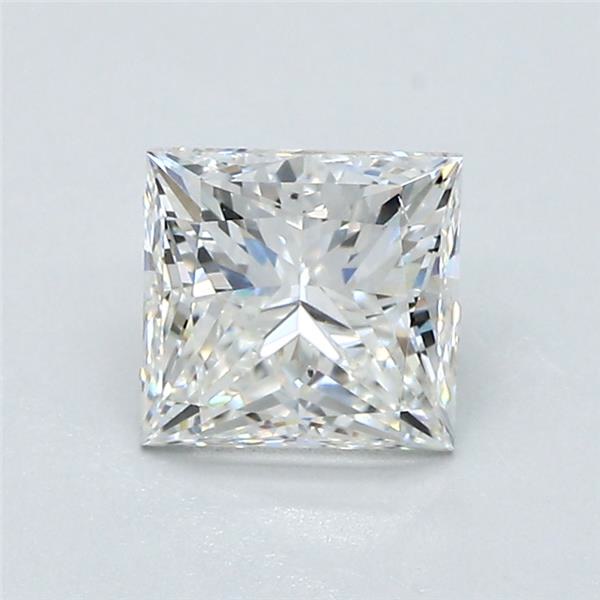
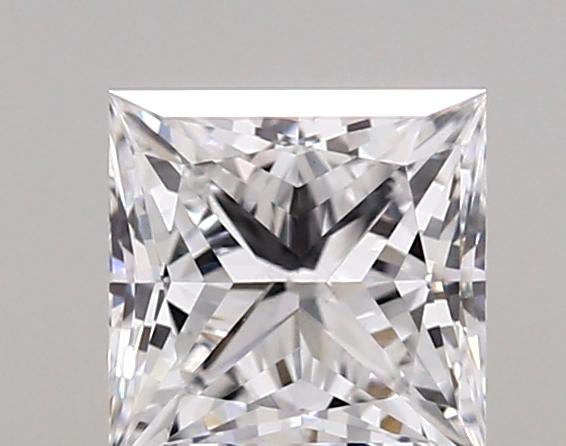
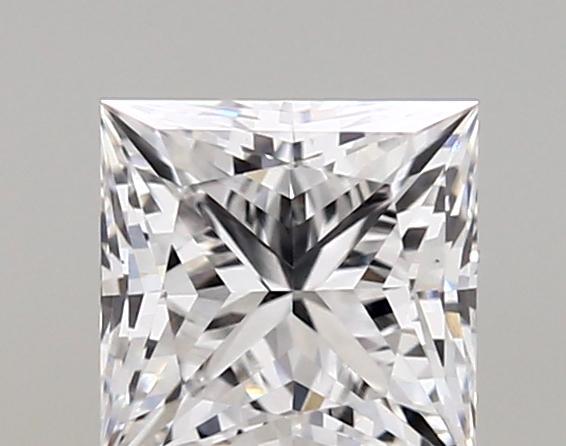
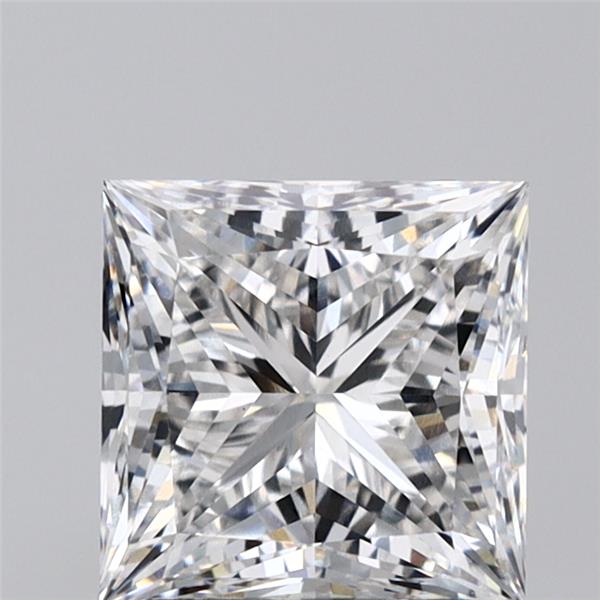
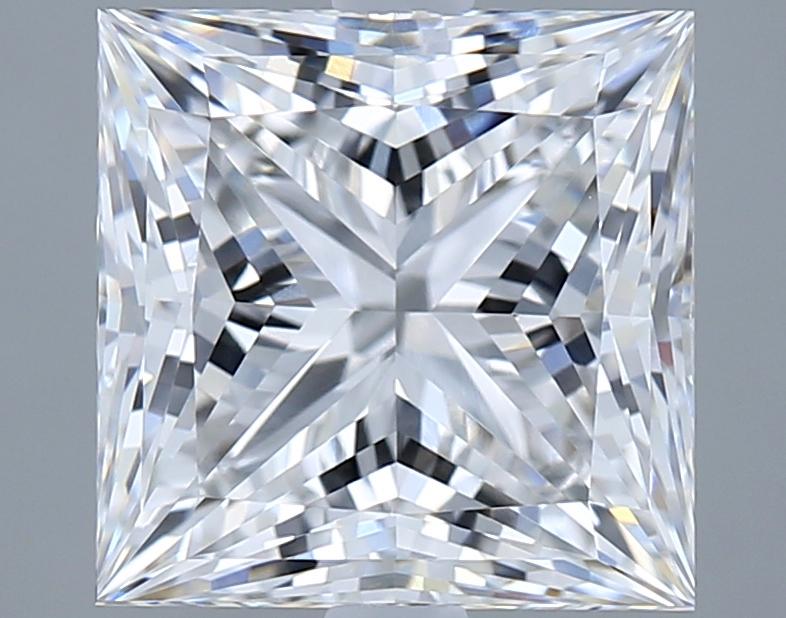
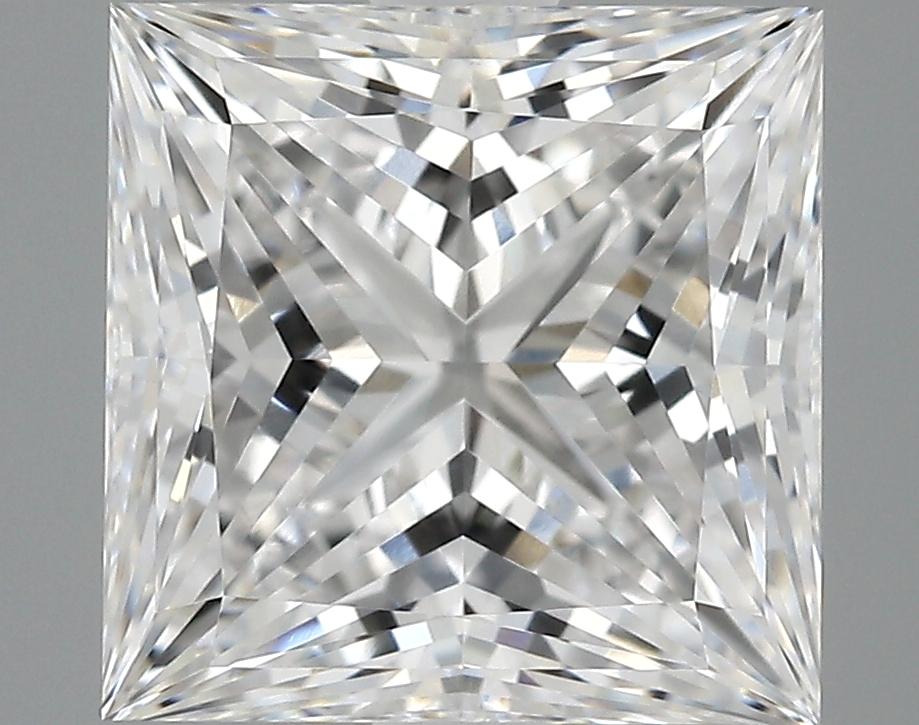
Select a Diamond
-
$1,897.02
-
$4,174.25
-
$1,020.92
-
$1,020.92
-
$980.88
-
$964.44
-
$1,002.88
-
$3,177.76
-
$5,330.08
-
$2,398.12
of 10 Diamonds Saved
| Diamond | Cut | Color | Clarity | Carat Weight | Grading Reports | Price | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| See Details | See Details | Unavailable | Remove This Item |
Check this box to add to your saved diamonds